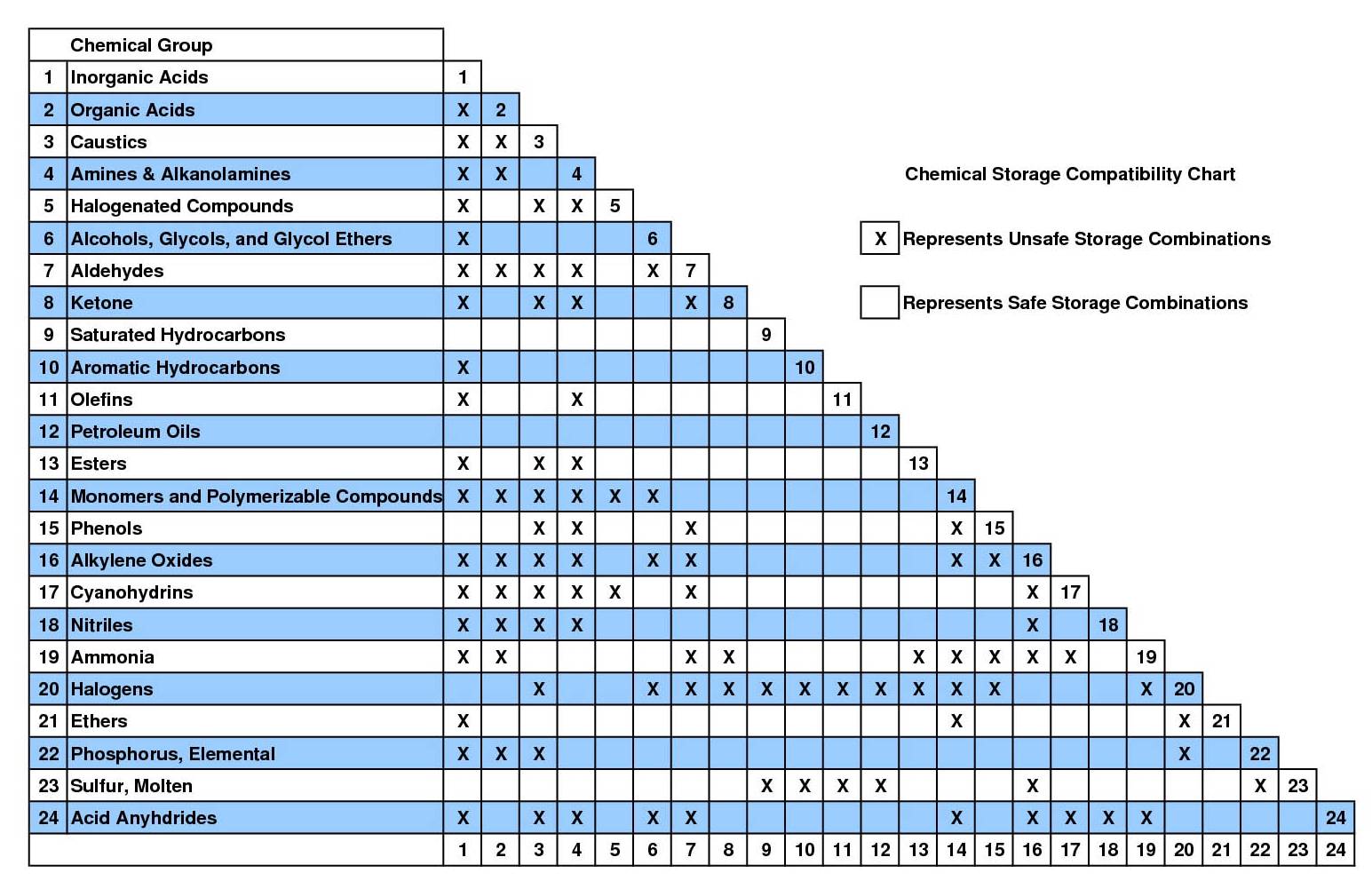
Incompatible Chemicals
The following chart is a quick reference of incompatibilities for many chemicals commonly encountered in the laboratory. It is not a comprehensive list of all possible combinations and chemicals. For details on any chemical, check the MSDS. If you need help reading the chart, please call 435-797-2892.
- Acetic acid with chromic acid, ethylene glycol, hydroxyl compounds, nitric acid, perchloric acid, permanganates, peroxides
- Acetone with concentrated sulfuric and nitric acid mixtures, hydrogen peroxide
- Acetylene with copper (tubing), bromine, chlorine, fluorine, iodine, silver, mercury and their compounds
- Alkali metals (e.g. powdered aluminum or magnesium, calcium, lithium, potassium, sodium) with carbon dioxide, carbon tetrachloride, chlorinated hydrocarbons, flammable liquids, oxidizers, salt sulfur, water
- Ammonia (anhydrous) with mercury, halogens, calcium hypochlorite, hydrogen fluoride
- Ammonium nitrate with acids, metal powders, flammable fluids, chlorates, nitrates, sulfur, and finely divided organics or combustibles materials
- Aniline with nitric acid, hydrogen peroxide, inorganic acids, oxidizers
- Bromine with ammonia, acetylene, benzene, butadiene, butane, petroleum gases, hydrogen, sodium carbide, turpentine, and finely divided metals
- Chlorates with ammonium salts, acids, metal powders, sulfur, finely divided organics or combustible materials
- Chromic acid with acetic acid, naphthalene, camphor, alcohol, glycerol, turpentine, and other flammable liquids
- Chlorine with ammonia, acetylene, butadiene, benzene, and other petroleum fractions, hydrogen, sodium carbide, turpentine, and finely divided powdered metals
- Cyanides with acids
- Hydrocarbons, general with fluorine, chlorine, bromine, chromic acid, sodium peroxide
- Hydrogen peroxide with copper, chromium, iron, most metals or their respective salts, flammable fluids, and other combustible materials, aniline, and nitromethane.
- Hydrogen sulfide with nitric acid, oxidizing gases
- Iodine with acetylene, ammonia (anhydrous or aqueous)
- Mercury with acetylene, ammonia, fulminic acid, hydrogen
- Nitric acid with acetic, chromic, and hydrocyanic acids, aniline, hydrogen sulfide, flammable liquids or gases and substances which are readily nitrated
- Oxalic acid with silver, mercury and their salts
- Oxygen with oils, grease, hydrogen, flammable liquids, solids and gases
- Perchloric acid with acetic anhydride, bismuth and its alloys, alcohol, paper, wood and other organic materials
- Phosphorous pentoxide with water, alcohols, strong bases
- Potassium permanganate with glycerol, ethylene glycol, benzadehyde, sulfuric acid
- Sodium peroxide with any oxidizable substances (e.g. ethanol, methanol, glacial acetic acid, acetic anhydride, benzaldehyde, carbon disulfide, glycerol, ethylene glycol, ethyl acetate, methyl acetate, furfural)
- Sulfuric acid with chlorates, perchlorates, permanganates, and water

